Hand And Mouth Disease In Adults
Children who develop hfmd should be kept home from school while they have symptoms and should avoid close contact with other kids for a few weeks afterward.
Hand and mouth disease in adults. Less often other enteroviruses are to blame. From the same virus that caused your other symptoms. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
Hand foot and mouth disease is often caused by a strain of coxsackievirus most commonly coxsackievirus a16. Visit the us department of agriculture national agricultural library to learn about foot and mouth disease. Some cases are caused by a different but related virus called enterovirus 71.
Hand foot and mouth disease is often confused with foot and mouth disease also called hoof and mouth disease which affects cows sheep and pigs. Hand foot and mouth disease hfmd is due to an infection that usually causes a typical illness including a typical rash. Oral ingestion is the main source of coxsackievirus infection and hand foot and mouth disease.
The coxsackievirus is part of a group of viruses called enteroviruses. It typically begins with a fever and feeling generally unwell. The coxsackievirus belongs to a group of viruses called nonpolio enteroviruses.
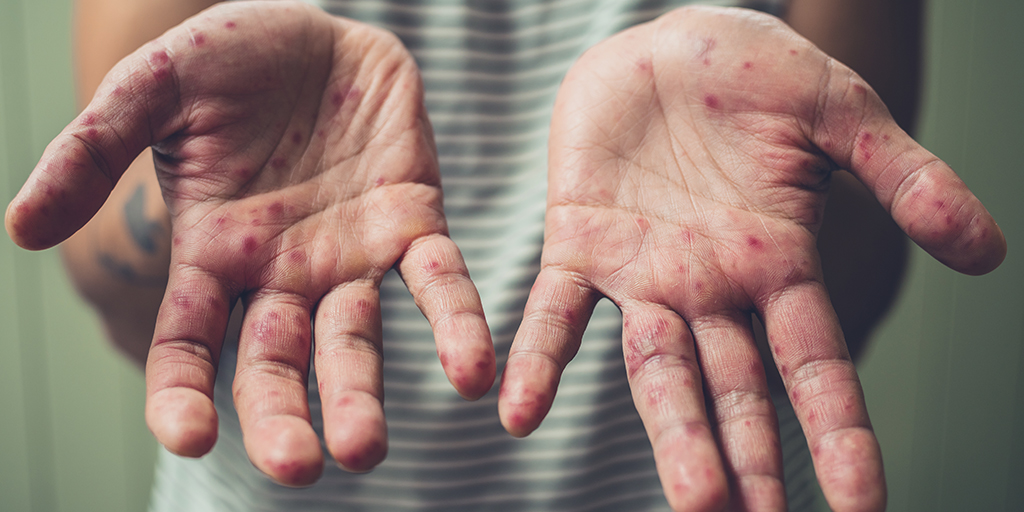
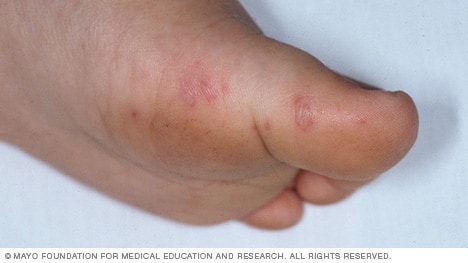
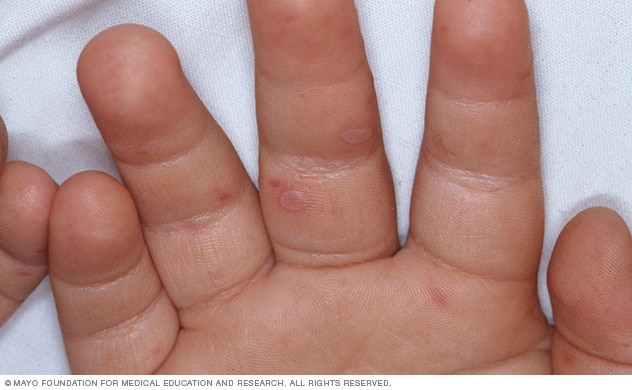
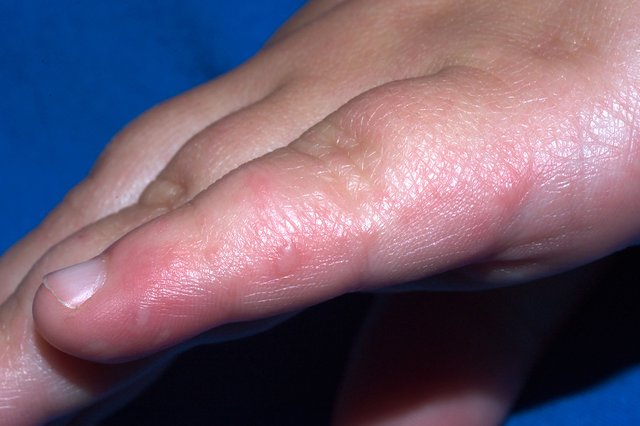
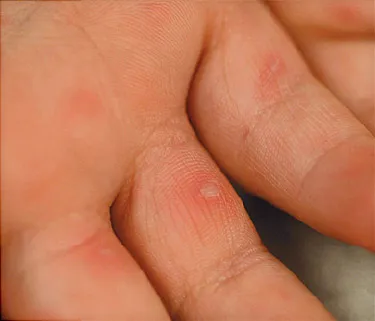
This is followed a day or two later by flat discolored spots or bumps that may blister on the hands feet and mouth and occasionally buttocks and groin. Hand foot and mouth disease hfmd is one such common childhood disease. Although hfmd is usually mild and self limited in both children and adults it is possible for the presentation to be much.
Cleveland clinic is a non profit academic medical center. Other types of enteroviruses sometimes cause hand foot and mouth disease. Symptoms of hand foot and mouth disease in adults.
Rarely the same illness is caused by other strains of coxsackievirus. Humans do not get the animal disease and animals do not get the human disease. Hand foot and mouth disease hfmd is a common infection caused by a group of viruses.
Hand foot and mouth disease hfmd is a common human syndrome caused by highly contagious intestinal viruses of the picornaviridae family typically characterized by a mild fever followed by a rash of flat discolored spots and bumps that may involve the skin of the hands feet and oral cavity. It is most commonly caused by the coxsackie a16 virus.